If the amplifier is the heart of a hi-fi system, the loudspeakers are its soul. Or something like that. Metaphors aside, one thing is sure: For truly enjoyable music playback, an amplifier that can deliver a quality audio signal is only as good as a loudspeaker that can do justice to that signal.
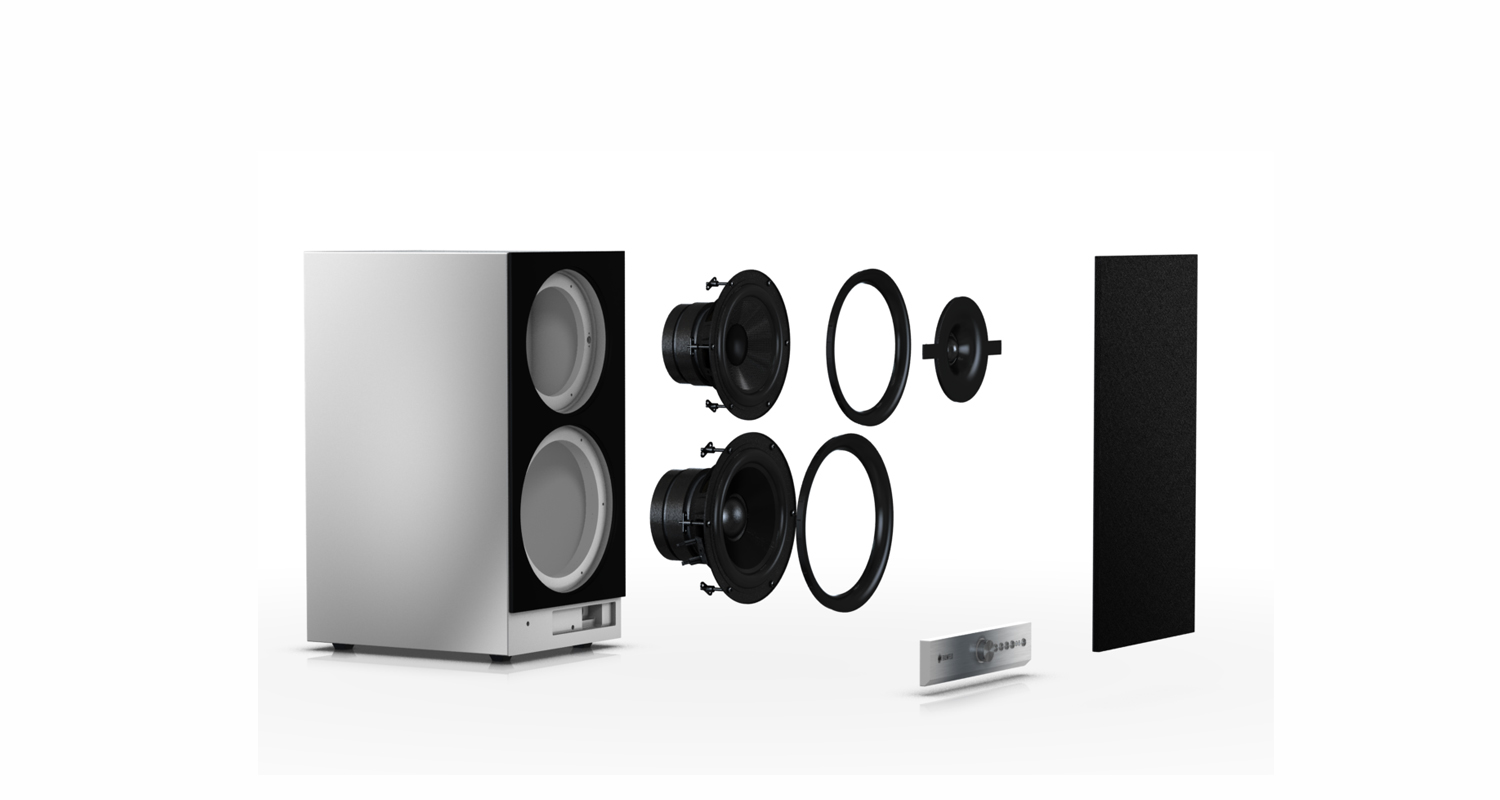
Within a speaker, it’s the drivers that turn an audio signal into hi-fi playack. Different loudspeakers employ different types of drivers in varying combinations, but the most common combination is: A bass driver (also called a woofer), a midrange driver and a tweeter. Some speakers also use so-called broadband or full-range drivers capable of reproducing the entire frequency range, but the following is dedicated to drivers that specialize in reproducing specific ranges.
Specialty drivers for different types of speakers
Since the 1960s, the use of three separate drivers – bass drivers, midrange driver, and tweeter – has become established with hi-fi stereo speakers, but many other loudspeaker driver combinations are possible. While one rarely finds loudspeakers that employ super tweeters, midbass drivers are, for instance, quite common and are used whenever there is not enough space within a loudspeaker enclosure for three separate units.
The Raumfeld One SOpens in new tab, for instance uses a midbass driver and tweeter in a coax arrangement in order to generate a maximum of rich sound from a small enclosure.
The most common drivers are as follows:
• Super tweeter: 10.000 to 20.000 Hz
• Tweeter: 2.500 to 20.000 Hz
• Mid-tweeter: 400 to 20.000 Hz
• Midrange driver: 400 to 2.500 Hz
• Midbass driver: 40 to 2.500 Hz
• Bass driver: 40 bis 400 Hz
• Subwoofer: 30 bis 150 Hz
• Full-range driver: 40 bis 20.000 Hz
All good things come in threes: Classic 3-way speakers
Most hi-fi speakers contain at least two separate drivers dedicated to distinct ranges in the frequency spectrum — so-called 2-way systems. 3-way systems are more commonly found in classic floor-standing stereo models, each containing at least three dedicated drivers: One for the treble, one for the midrange and one for the bass. Some, like Teufel’s Ultima 40 Mk2 contain more than one woofer for the bass range for enhanced performance. This is still a 3-way system but with four drivers. It’s also common to find 3-way speakers with multiple midrange drivers such as the Focal Grande Utopia EM.
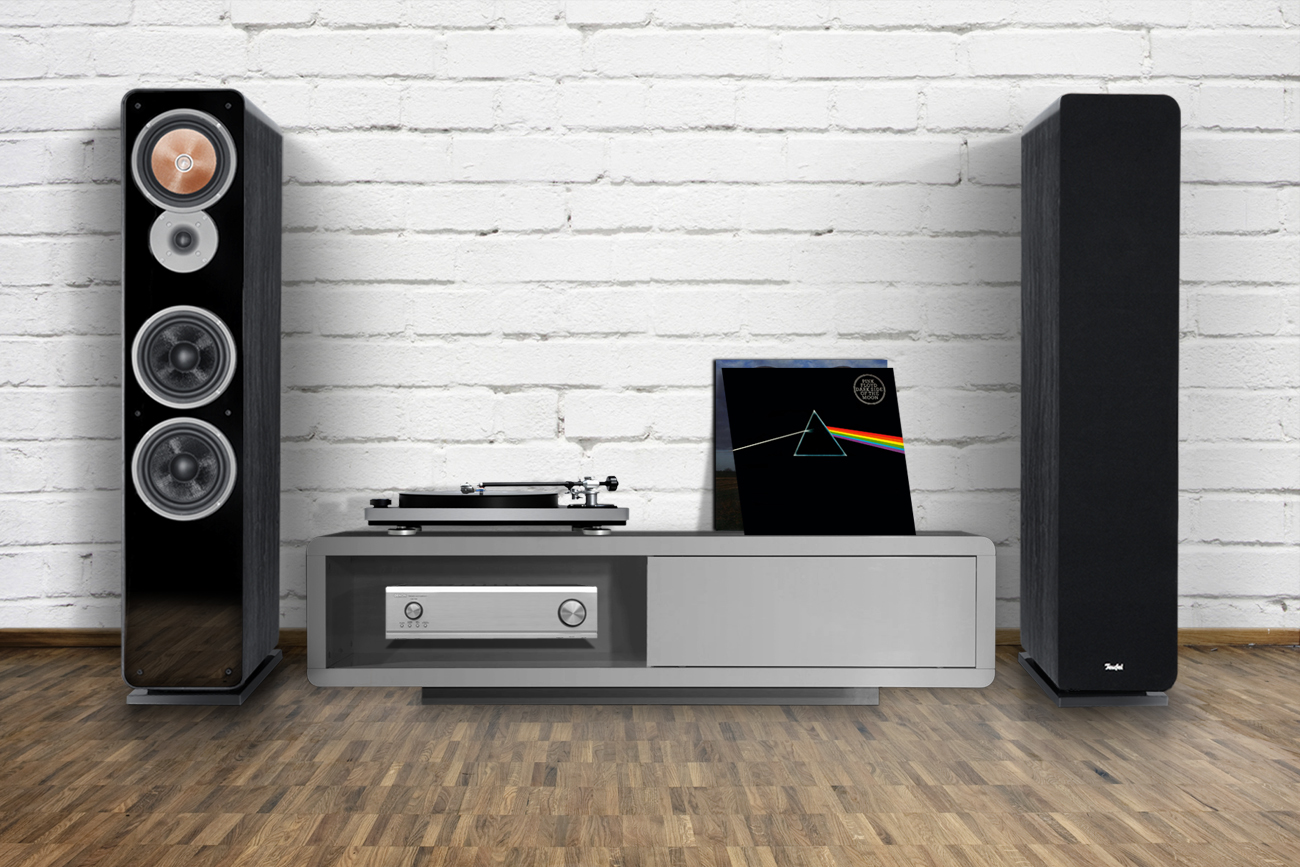

The reason classic floor-standing stereo speakers tend to use 3-way driver arrangements is to completely and evenly cover the entire frequency range found in music, most of which will contain bass, mids and treble along the range of human hearing which extends from about 20 Hz to 20 kHz. While a full-range driver can play back the full range, drivers dedicated to a specific range of frequencies generally produce sound with more clarity and power. A full-range driver will, in particular, have difficulty with the highest and lowest frequencies. There are full-range drivers capable of covering the entire range with undiminished sound quality, but they are more expensive than the use of separate drivers dedicated to a certain range and so usually reserved for devices like soundbases where space is limited.
2-way arrangments for classic bookshelf speakers
Bookshelf speakers are the perfect compromise for people who love music, but who don’t necessarily have the space for a pair of tower speakers. As their name would suggest, bookshelf speakers are small enough to be stowed on a shelf. Like any speaker, they come in a wide range of price and quality levels.
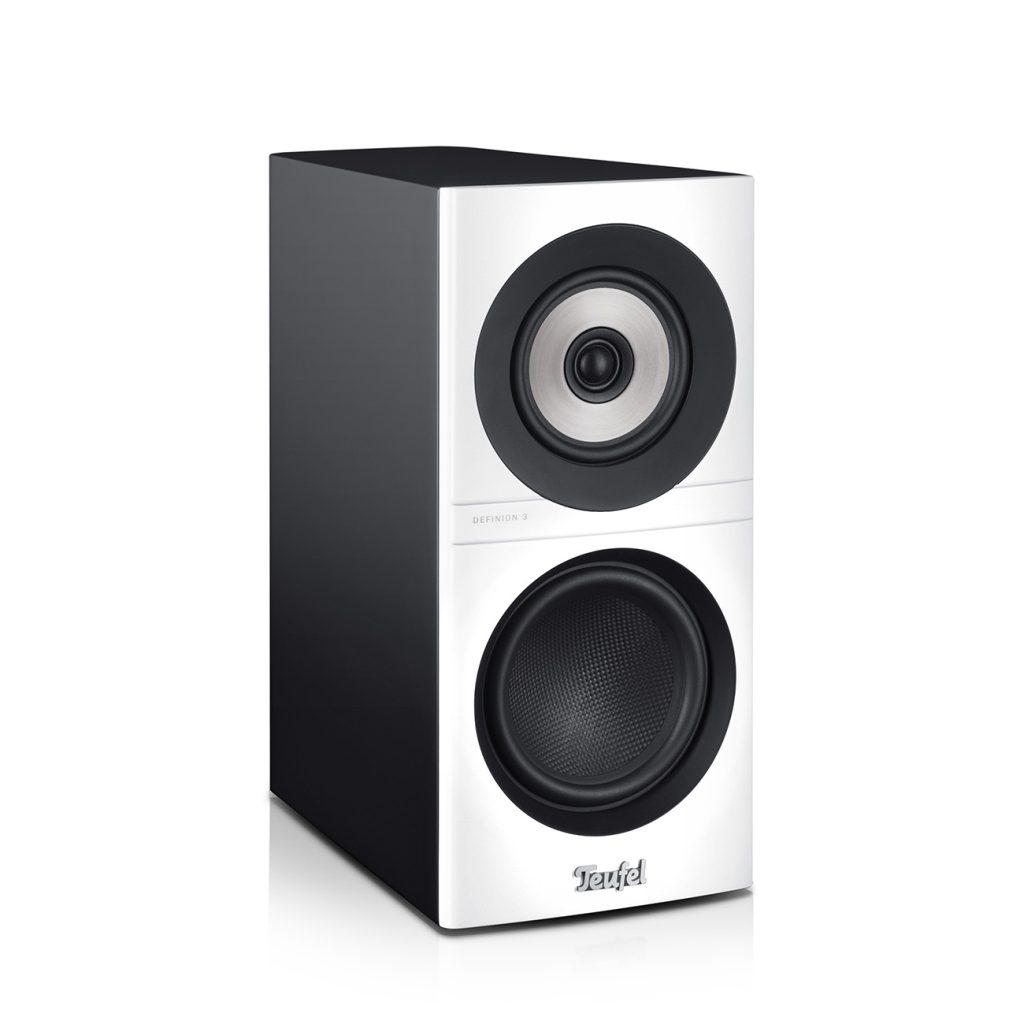

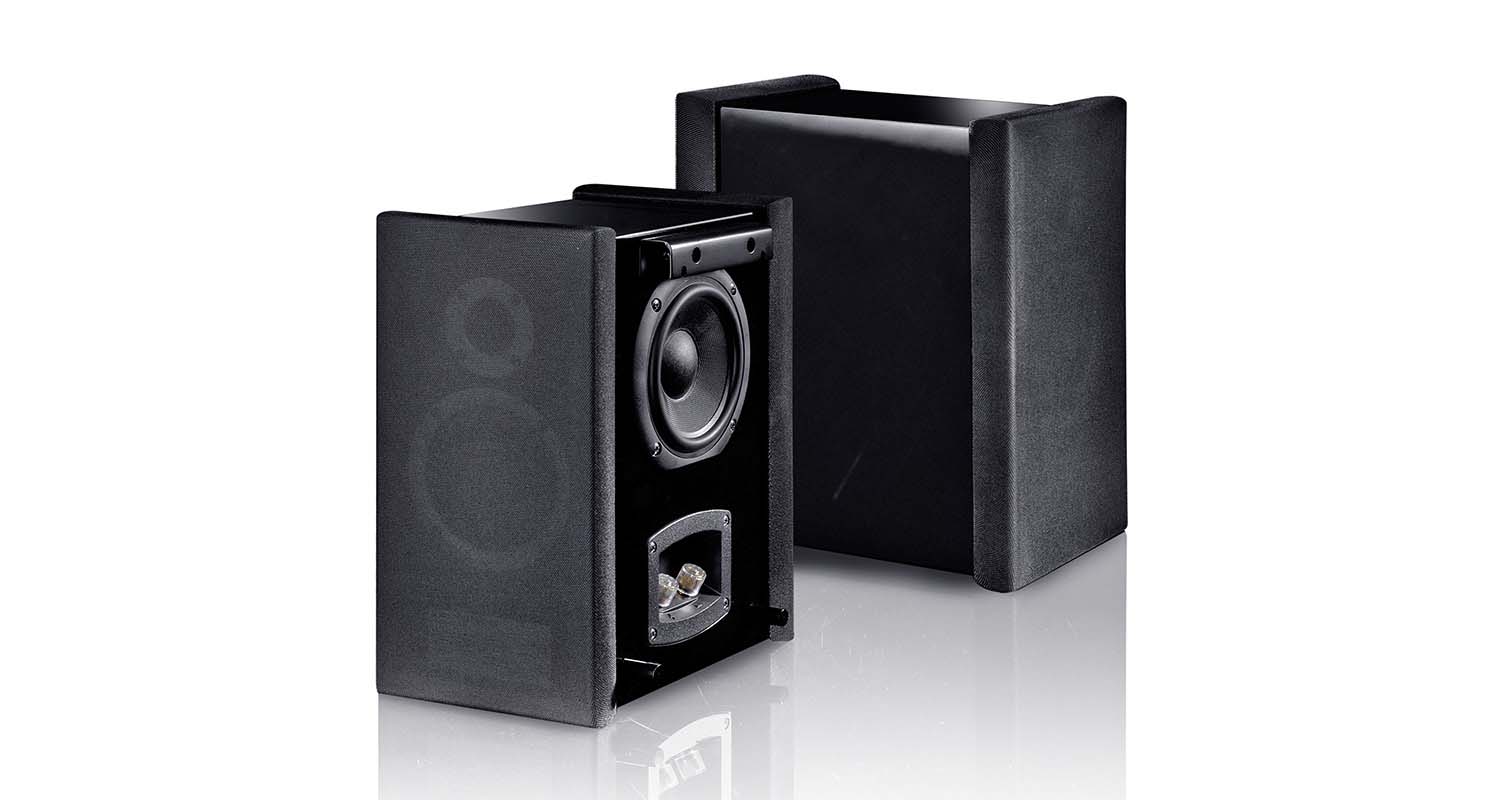
Hi-fi bookshelf stereo speakers distingish themselves by the superior audio components used starting with the drivers. Unlike less expensive bookshelf speakers, hi-fi models generally employ a combination of tweeters and midrange or midbass drivers in a 2-way construction as this will allow the speaker to play back a broader frequency range with more accuracy. A midbass driver will, of course, not be able to produce the bone-rattling lows of a subwoofer, but it is completely sufficient for most music playback.
Additional types of speakers: Satellites and soundbars
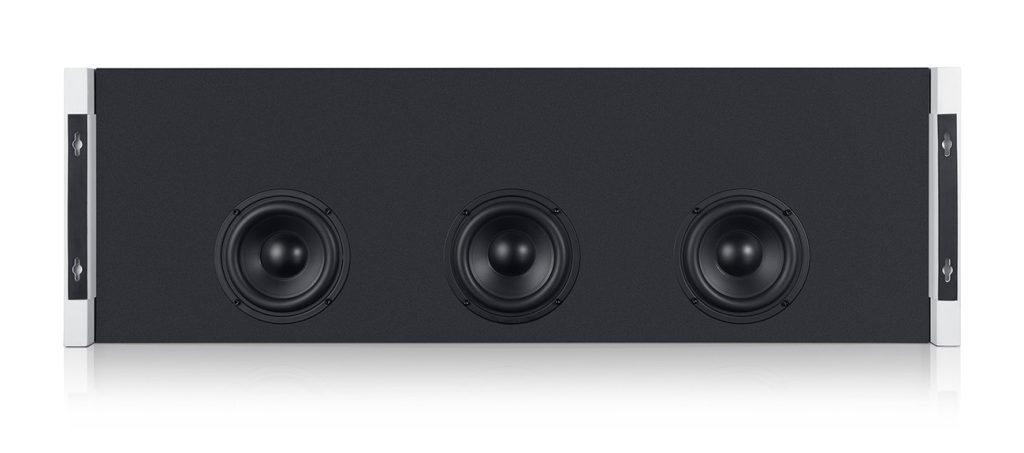
Floor-standing stereo speakers and bookshelf speakers are common in the hi-fi world, but there are many other types of speakers. More commonly in home cinema, the low bass frequencies are produced by completely separate loudspeakers. In a 5.1 home cinema set, the “.1” stands for the single subwoofer that accompanies the system and is responsible for the entire low end. This takes the burden off the satellite speakers which only have to reproduce the mids and treble tones. Since they don’t have to accommodate large woofers, satellites can have much smaller enclosures than typical floorstanding stereo speakers.
Some even employ coax technology to increase the amount of drivers that can be accommodated in a small space. Teufel’s CubyconOpens in new tab, for instance, is a 2-way system with a total of 3 drivers: 1 tweeter and 2 midrange drivers. One of the midrange drivers sits directly behind the tweeter which not only saves space, but leads to a superior sound dispersion.
When it comes to soundbars and soundbases, there is a wide range of driver technology employed. Some contain up to six different drivers from classic tweeters and midrange drivers to midbass drivers. Others, like the Teufel Cinebase Opens in new tabmakes use of 6 high-end full-range drivers arranged in a row. This saves space, allowing system to remain relatively flat. Two downward facing woofers built into the bottom of the enclosure ensure that all movie, television and music playback is accompanied by highly realistic and very good bass. In short, with soundbars and soundbases, all combinations are possible and can produce excellent sound from a single enclosure.
Conclusion: When purchasing loudspeakers, pay special attention to the drivers
This article will hopefully have awakened your interest in one part of a loudspeaker’s inner workings and rendered the loudspeaker specs a little more understandable. If one is looking at a small all-in-one speaker that contains a tweeter and midbass driver, it is wise to keep expectations low when it comes to bass playback. Yet some all-in-one speakers like the Teufel Cinebase or the Raumfeld One MOpens in new tab contain bass drivers built into the bottom of the enclosure. This allows a relatively compact speaker to produce a big bass sound, much deeper and more powerful than expected. For this reason, one should always be sure to check the driver specifications listed for any speaker before buying.